Less than 5 years to build the European Open Science Cloud
There are decades of lessons learnt and resources to build upon … where does the EOSCpilot project fit in?
According to a recent article in The Economist, the world’s most valuable resource is no longer oil, but data. Today Europe is the largest worldwide producer of scientific data, but an insufficient and fragmented infrastructure means that data is not being exploited to its full potential.
This represents just one of a number of the current challenges posed for Europe, along with inadequate awareness on the value of data and the incentives for data sharing, lack of common standards hindering the interoperability of data, and insufficient hardware capacity for scientific computing, storage, and connectivity. In addition, there is a real need to address the fragmentation and lack of coordination over different scientific communities and countries and to translate recent changes in privacy, data protection and copyright rules to the research data domain.
But this is where the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC) comes into play, to strengthen Europe's position in data-driven innovation, to improve competitiveness and cohesion and to help create a Digital Single Market. EOSC has the mission to create a federated, globally accessible, multidisciplinary environment where researchers, innovators, companies and citizens can publish, find, use and reuse each other's data, tools, publications and other outputs for research, innovation and educational purposes.
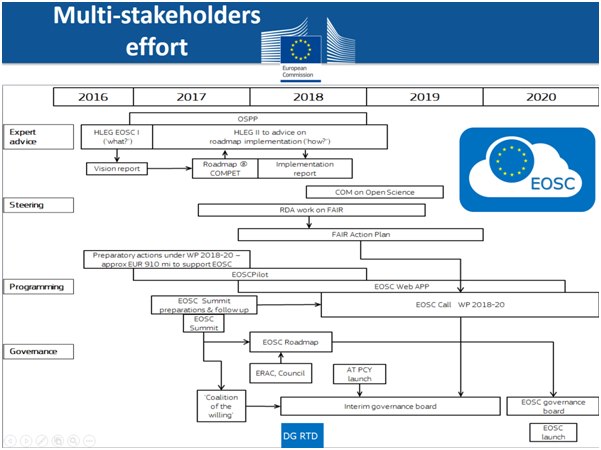
As highlighted during the recent EGI Conference 2017 and INDIGO Summit 2017 to realise the overall vision of the EOSC there are a series of concurrent and subsequent activities in the pipeline. The European Commission has an ambitious plan and five-year timeline for the realisation of the European Open Science Cloud.
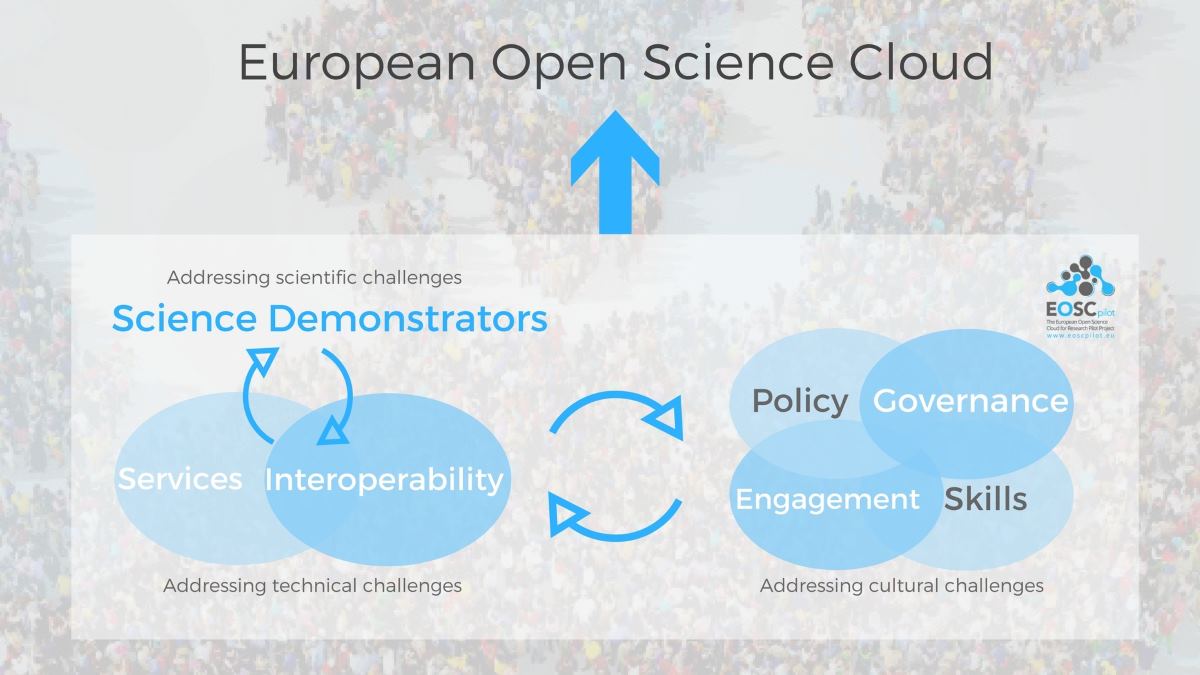
As part of this picture, the EOSCpilot (2017-2018) project supports the first phase in the development of the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC) by:
- Proposing and trialling the governance framework for the EOSC and contributing to the development of European open science policy and best practice;
- Developing a number of demonstrators functioning as high-profile pilots that integrate services and infrastructures to show interoperability and its benefits in a number of scientific domains; and
- Engaging with a broad range of stakeholders, crossing borders and communities, to build the trust and skills required for adoption of an open approach to scientific research.
The science demonstrators will help define the infrastructure needed by European researchers, while showing the scientific excellence and societal impact that EOSC could achieve. In the words of the project coordinator, Juan Bicarregui from the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC), “EOSCpilot will deliver a number of building blocks, including technology demonstrators and a first draft of a multi-stakeholder structure which can accommodate a mix of different users.”
With the start of the EOSCpilot project in January 2017, 5 science demonstrators began their activities:
- Environmental & Earth Sciences - ENVRI Radiative Forcing Integration to enable comparable data access across multiple research communities by working on data integration and harmonised access
- High Energy Physics - WLCG: large-scale, long-term data preservation and re-use of physics data through the deployment of HEP data in the EOSC open to other research communities
- Social Sciences – TEXTCROWD: Collaborative semantic enrichment of text-based datasets by developing new software to enable a semantic enrichment of text sources and make it available on the EOSC.
- Life Sciences - Pan-Cancer Analyses & Cloud Computing within the EOSC to accelerate genomic analysis on the EOSC and reuse solutions in other areas (e.g. for cardiovascular & neuro-degenerative diseases)
- The photon-neutron community to improve the community’s computing facilities by creating a virtual platform for all users (e.g., for users with no storage facilities at their home institutes)
Ten further science demonstrators will be implemented over the lifetime of the project through two calls. The first of these calls was open in April 2017 and received 30 applications across the following areas – Biomedicine, Astronomy and Astrophysics, Earth Sciences, Humanities & Social Sciences, Energy Physics and Generic Technologies. Five will be selected from these to start on 1st July and a further five will be on-boarded through a call due to open in the second half of 2017.
The European Open Science Cloud for Research pilot project (EOSCpilot) www.eoscpilot.com is funded by the European Commission, DG Research & Innovation under contract no. 739563.
http://www.economist.com/news/leaders/21721656-data-economy-demands-new-...
